Lumbar osteochondrosis is a degenerative disease of the vertebrae and intervertebral discs. It is widely believed that lumbar osteochondrosis affects the spine itself as well as the nerves and blood vessels. Thus, the symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis are divided into those that affect the spine itself - they are called vertebral/vertebral syndromes - and those that appear outside the spine, involving nerve and vascular structures - they are called non-vertebral/vertebral syndromesExtravertebral syndrome. Extravertebral, in turn, is subdivided into reflex and radicular syndromes. Since the term "syndrome" implies a group of symptoms, it can be simplified to say that the symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis consist of three groups - vertebrae, reflexes, and nerve roots.
Vertebral symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis
- Violation of the configuration (curvature) of the spine;
- lower back muscle tension;
- Violation of lower back mobility;
- Localized back pain.
Reflex symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis
The main reflex symptom is back pain. It can be sudden or permanent. Pain occurs after physical activity or clumsy movement. For example, when turning, leaning or lifting weights. Muscle tension and stiffness of movement occur - more common in the morning. Gunshot wound to lower back or leg. Impaired sensitivity in the lower extremities - numbness, goose bumps, tingling or burning. Changes in gait and coordination. Increased sweating. The work of the bowel and bladder is often disturbed. There is a malfunction in the working of the internal organs. Impaired sexual function. Sleep is disturbed by pain. Mood swings, irritability, and fatigue occur. Depression sometimes occurs.
Aggravating factors are physical exertion, prolonged uncomfortable postures, hypothermia, and stress.
Pain reflex symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis are generally classified into low back pain, low back pain, and low back pain, depending on the severity and location of the process.
- Low back pain (low back pain)is the most severe pain. Provocation is an awkward gesture, sneezing, coughing. To relieve the condition, the patient involuntarily leans forward or bends over. Trying to straighten up can lead to new back pain.
- low back pain- Pain "tolerable" pain with worsening episodes. Over time, it can develop into persistent, severe pain.
- sciatica- Pain extending from the lower back to the legs.
Root symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis
They occur due to effects on the nerves that come out of the spine.
There are many nerves coming out of the spine. They are called spinal nerves. Each of these nerves branched off gradually, with well-defined boundaries along a certain area of the body. This area is called the segmental innervation area. Each vertebra, disc, nerve and region is numbered strictly correspondingly. If a nerve is affected, symptoms will appear in the segmental innervation area corresponding to that nerve, not just anywhere - anywhere.
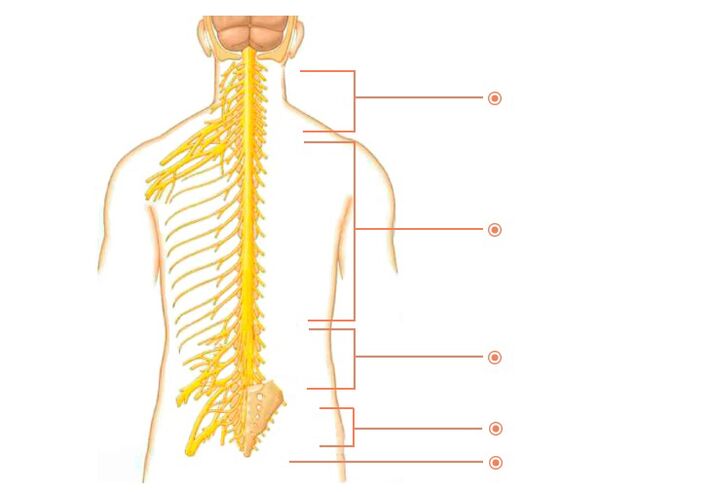
spinal nerve
Root symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis include:- Reduced or lost reflexes;
- muscle weakness;
- breach of sensitivity;
- Root pain.
Not all areas of the lumbar spine are equally susceptible to pathology. The most liquid segments are affected more often: L3-L4, L4-L5 and L5-S1. According to the principle - "more movement - more wear".


Innervation area of lumbar vertebrae
Osteochondrosis L3–L4- Acts on spinal nerve L4. Main signs: knee jerk weakness. Pain, numbness, and decreased sensitivity can affect the front of the thigh.
Osteochondrosis L4–L5- Acts on spinal nerve L5. Main signs: Weakness of the muscles that lift the big toe and foot. It is difficult for the patient to keep their heels standing. Pain, numbness, and decreased sensitivity "along the stripes" from the lower back to the buttocks and thighs, then through the calves, gradually moving to the front and ending at the first three toes of the foot.
Osteochondrosis L5–S1- Acts on the spinal nerve S1. Main signs: calf muscle weakness. The patient has difficulty maintaining a standing on tiptoe. Pain, numbness, and decreased sensitivity are detected from the hip, then along the back of the thigh and calf, moving to the side of the foot and little finger.
Occasionally, lumbar osteochondrosis affects not only the nerves, but also the nerve root arteries. This threatens the development of the most dangerous pathology - spinal stroke, with serious consequences for the person - paralysis and paralysis, as well as severe dysfunction of the pelvic organs.
Symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis:
- depending on the stage of osteochondrosis;
- Aggravated by tilting and rolling;
- More often after 30-35 years;
- Women are about 3 times more likely than men.
You certainly noticed that the radicular symptoms were well defined and the reflex symptoms were very vague and vague. As you know, everything that isn't clearly defined serves as a handy cover for professional helplessness. This applies, among other things, to reflex symptoms and physician-favorite concepts like "age-related changes. "Many of you are sure to be familiar with this situation when a doctor explains the problem through a "reflex" or "age-related" process. Most people rightly think at a time like this that the doctor simply can't figure out what's going on, and is trying to hide his incompetence in the fog of these "magic words".
There used to be a catchphrase: "Every accident has a first name, a last name, and a job title. " Every disease has its own unique symptoms. And the doctor's job is to know them clearly. Then there's no need to get fascinated any more and blame everything on osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. Now you understand how important it is to find an experienced and knowledgeable doctor. The outcome of correct diagnosis and treatment depends on this.
When choosing a clinic, the main thing is to find an experienced and knowledgeable doctor.
Diagnosis of lumbar osteochondrosis
To date, there are many modern hardware diagnostic methods for osteochondrosis. The most accurate of these are MRI and CT. But the primary method remains clinical diagnosis -- which is when an experienced doctor compares data from at least three sources -- from the patient's complaints, MRI results and symptoms he finds during the exam. This allows you to make the most accurate diagnosis and develop an effective personal treatment plan.
Treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis
As you know, osteochondrosis is a real "tangle" symptom, untie it and your doctor will save you pain and suffering. But it is not possible to eliminate changes in the vertebrae and discs. Therefore, the term "treatment of osteochondrosis" must be properly understood. If you are interested in eliminating pain and other suffering, then yes - it is very possible. And if you have an academic discussion on the topic of restoring vertebrae and discs "like a newborn child", then no, the past cannot be returned to the past. You need to be realistic so you don't fall for the bait of scammers.
Don't fall for the bait of liars!
It is impossible for the vertebrae and intervertebral discs to return to their original shape!
What is the main treatment?
Soft manipulation is the main treatment method for lumbar osteochondrosis. It's like an antibiotic for pneumonia - you can't live without it. Other types—massage, medication, physical therapy, and exercise therapy—are complementary.
How does gentle manual therapy work?
The nutrition of the intervertebral disc is directly related to the muscles surrounding the lumbar spine. In addition, the psoas muscle itself is one of the constituent causes of lumbar osteochondrosis pain. Soft Manipulation is a special method that restores your muscles to their natural physiological state, eliminating spasms, muscle clamping and improving disc nutrition.
The disc is the only part of the body without blood vessels and is nourished by the normal functioning of the muscles.
Additionally, when treating with hands, chiropractors:
- Remove load from affected vertebrae and discs and distribute them correctly
- relax muscles and help them return to normal
thereby:
Manual shocks mobilize the body's internal forces and initiate self-healing mechanisms. Treatment is absolutely safe.
The clinic uses all soft manipulation methods:
- Patient unclamped
- increase drive
- Restoring the body's motor function
normalize blood circulation
A doctor's qualification in any specialized clinic will give you the freedom to use all of these methods for the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis. Furthermore, in each case, we combine them, taking into account synergistic effects.
Synergy is not just a bunch of different effects, it's the right order in a combination of methods. Synergy can improve the quality of treatment. A simple example of synergy is our hands. How long does it take to button a button? second? ! If you do it with one hand, you can't do it in a minute. That is, moving with two hands is not twice as fast as with one, but many times faster. And listen to the same music played by a single instrument or an entire orchestra - is there a difference? That's the effect of synergy - it gets everything done more powerful, more efficient, faster, but at the same time - more discreet.
Complementary Therapies - Medication, Massage, Physiotherapy and Exercise Therapy
Treat with medication.In the treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis, drugs with various action spectrums are used. These are medications that relieve swelling, inflammation, and pain in deep tissues. Medicines that improve blood circulation. Also, use drugs that help restore damaged disc cartilage tissue and compressed nerves - chondroprotectants and B vitamins. If necessary, medication is prescribed by a chiropractor in combination with other treatments.
massage.As you know, massage can bring pleasure, massage can heal. Recreational massages are performed at spas and therapeutic massages are performed at medical clinics. In clinics, medical massages are performed during gentle manual treatments. To increase the effectiveness of manual therapy and normalize metabolic processes - it can all be a therapeutic massage!
physiotherapy.There are many physiotherapy methods for the treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis, such as ultrasound, electrophoresis, laser and so on.
physiotherapy- Include regular gymnastics to strengthen muscles. The most important thing is to do the right exercises without sudden movements. During treatment in a specialist clinic, your doctor will recommend necessary exercises for you. Pilates is the best option.
Prevention of lumbar osteochondrosis
To avoid relapse, create comfortable sleeping and working conditions for yourself. Pay attention to your weight and proper nutrition. Keep your body active. But most importantly, don't neglect your health and don't save money. Don't let things go by themselves. After recovery, try a maintenance period of gentle manual therapy at least once every three to six months - this will reduce risk factors. Don't forget that neglected osteochondrosis can lead to complications - herniated and herniated discs. Remember: your health, first and foremost, you need!
Running osteochondrosis can lead to complications - herniation and disc herniation.
Benefits of treating osteochondrosis in a specialist clinic:
- Comprehensive and qualified treatment is guaranteed. The word "complete" is key to our work.
- We consider each case individually and comprehensively - without formalism.
- synergistic effect.
- Guaranteed honest and fair prices.